Marketing & Promotion
Endless Possibilities with Geomagnetic Indoor Positioning
Tuesday, May 17, 2016

|
Dan Patton |

If you’ve written or used commercial-grade GPS apps, you know they’re no longer limited to basic driving directions. Today, tons of cool apps put your phone's location awareness to good use - you can code a whole range of apps, from finding nearby restaurants to hailing taxis.
And these apps work well - as long as the mobile user is outside. However, once you cross the threshold into a building, GPS becomes largely useless.
This has led to the development of indoor positioning systems such as WiFi, radio and beacons, all of which require hardware – or the combination of multiple systems working together – to locate your position indoors. And their accuracy can only be increased at the expense of purchasing, installing and maintaining infrastructure equipment – a complete headache if you have a large venue or need to scale across multiple venues.
It’s no wonder there are countless GPS apps out there and only a handful of indoor positioning apps. Fortunately for developers, this is all quickly changing with the era of Geomagnetic indoor positioning.
What is Geomagnetic positioning and how is it paving the way for great location-based mobile apps?
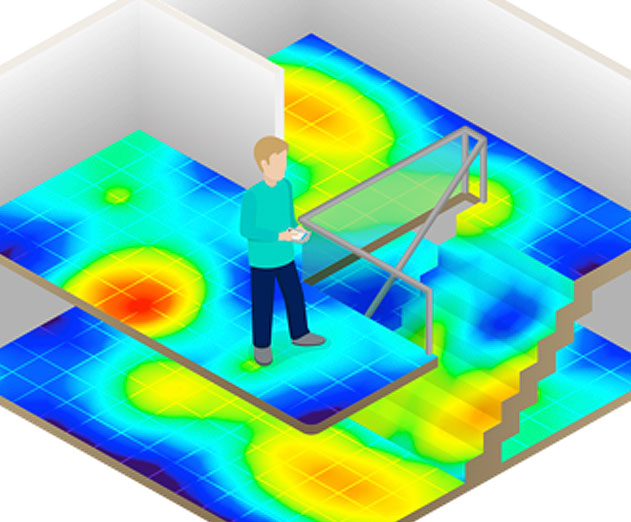
Geomagnetic positioning is a truly disruptive technology – for the first time, you have a way to pinpoint a person’s location indoors without the need to install additional infrastructures such as beacons or WiFi.
Here’s how it works. Modern buildings all have a unique magnetic landscape produced by the Earth’s magnetic field that interacts with steel and other materials found in structures of buildings. By utilizing the built-in magnetic sensor (the compass) as well as other sensing technologies within a smartphone, a team of researchers at Oulu University found that their software was able to use the magnetic field inside the building as a map to accurately pinpoint and track a person’s location indoors, with 1-2 meters accuracy.
Those researchers went on to found IndoorAtlas, a Finnish start-up that developed the world’s first and only ubiquitous indoor positioning Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) leveraging geomagnetic technology. The cloud platform interface and workflow was designed to enable you to easily create and map venues and then go on to build location-based services using their Android and iOS SDKs.
What’s more, Geomagnetic positioning doesn’t require the use of hardware, which is a challenge to scale across multiple venues. Just think about how many beacons you’d need to map out an entire mall to get 1-2 meters accuracy - likely thousands! The software is also able to utilize available signals and information sources for further optimization including movement sensors, WiFi, BLE and barometer.
What type of mobile applications are developers already creating with this technology?
The list of possibilities is endless with this type of technology depending on the customer requirement. Early adopters of location based services range from malls and airports to museums and hospitals. Most have the goal to increase the user experience and loyalty, and/or drive sales through proximity marketing.
Take for instance China’s leading internet search portal and map provider, Baidu. They are deploying IndoorAtlas’ location-based services to 270 million Baidu Maps users targeting malls, train stations, airports and other major venues across China. The goal is to help users navigate and search for stores/facilities and receive personalized offers, among other features.
Harry Potter fans will get a kick out of this. Consider Marauder’s magical map that ESRI UK developed and showcased at an event. What’s great about this example is that it demonstrates the impact that indoor positioning will have on society, such as social networking. Your app could connect multiple users together in a venue or even help a lost husband find his wife in a mall with a ‘find my buddy’ feature. Use cases like these only become possible when you have a scalable and accurate indoor positioning technology.
What type of use case features are being deployed using Geomagnetic Positioning?
Despite IndoorAtlas only being founded in 2012, over 25,000 developers across the world have signed-up to start piloting and building a variety of mobile app features using its Geomagnetic Indoor Positioning platform. Here are some popular location use case features:
- Way-finding/Navigation: Enables you to provide your users with navigation indoors - get them to a target location, which could be the shortest, the most convenient or the safest way.
- Search (Point of Interest Database): Help your users to locate a specific brand/ facility, search for a location in an unfamiliar environment like a booth or receive a targeted advertisement or offer based on search and location.
- Proximity Marketing: Help customers receive relevant, highly targeted and timely coupons/offers based on their indoor location.
- Multi-dot: Enables multiple users to be visualized on a map. This is great for social networking and team navigation as multiple devices can be located in real-time when using a mobile app.
How can developers start using the technology and platform to start building an app?
It’s simple. Developers just need to go to www.indooratlas.com and sign-up for a free account. From there, just follow the simple workflow steps:
- Step one: Create a location and add floor plans using the web tools on your desktop (and if the venue already exists publicly, you can jump straight to building your app with the available SDK).
- Step two: Fingerprint/map the venue. Using the mapping mobile tool, you can access the floor plans and collect sensor data throughout the venue using your smartphone (Android Nexus devices are recommended for the mapping stage). The collected data is uploaded to IndoorAtlas’ cloud platform where a landscape of sensor reading data from the venue is created for the positioning algorithm.
- Step three: While the sensor data is being collected via IndoorAtlas’ mobile app, the service is constantly analyzing the data to generate an updated lookup map, used for positioning. The results and quality analysis of the lookup map can be viewed in IndoorAtlas’ web portal - it shows how well the positioning is going to work. Publishing the updated lookup map is just a simple click from here.
- Step four: You can generate an API key and use IndoorAtlas’ SDK for Android and iOS and Android platforms to add location-based features to your mobile app. The API communicates with the positioning service that computes the device’s location and returns it back to your mobile app as GPS coordinates. You can also check out IndoorAtlas’ use case code examples to get you started quicker.
IndoorAtlas is continuously enhancing its platform and will be bringing new capabilities to market later this year. But for now, sign-up and get started - it’s an innovative technology and the use case possibilities are endless.
Read more: http://scopetrader.com/partner/link/?ref=Endless P
This content is made possible by a guest author, or sponsor; it is not written by and does not necessarily reflect the views of App Developer Magazine's editorial staff.

Become a subscriber of App Developer Magazine for just $5.99 a month and take advantage of all these perks.
MEMBERS GET ACCESS TO
- - Exclusive content from leaders in the industry
- - Q&A articles from industry leaders
- - Tips and tricks from the most successful developers weekly
- - Monthly issues, including all 90+ back-issues since 2012
- - Event discounts and early-bird signups
- - Gain insight from top achievers in the app store
- - Learn what tools to use, what SDK's to use, and more
Subscribe here










Comments